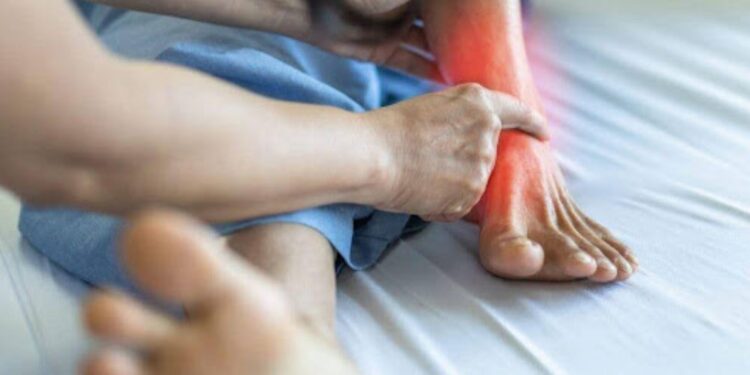
There still needs to be a lot of awareness of intravenous (IV) infiltration, a common complication during IV therapy. IV infiltration happens when fluid or medication leaks from the vein into the tissue around it instead of staying inside the vein. This can cause pain, swelling, and skin changes.
If not caught early, it can lead to serious complications like burns and tissue damage. Awareness is important so that patients and caregivers can recognize signs quickly and act to prevent further harm. In this blog post, the signs of intravenous infiltration, its risks, and what to do will be explained clearly.
Signs of Intravenous Infiltration
The signs of intravenous infiltration are important to recognize early. Here are some key signs of intravenous infiltration to watch for:
- Swelling or puffiness around the IV site
- Skin that feels cool or cold to the touch
- Skin discoloration, such as redness or paleness
- Pain, discomfort, or a burning sensation near the IV site
- Slow or stopped IV flow
- Numbness or tingling around or below the IV site
Early detection is important because infiltration can cause serious problems like tissue damage, infections, and nerve issues if left untreated. Recognizing these signs quickly can help prevent further harm and allow for prompt medical care.
How Does IV Infiltration Cause Burns and Tissue Damage?
In some cases, IV infiltration causes burns and tissue damage when the medication or fluid leaks out of the vein and into the surrounding tissue. Certain drugs and fluids are irritants or corrosive and can chemically damage the skin and deeper tissues. This damage can cause chemical burns, which may lead to redness, blistering, and pain.
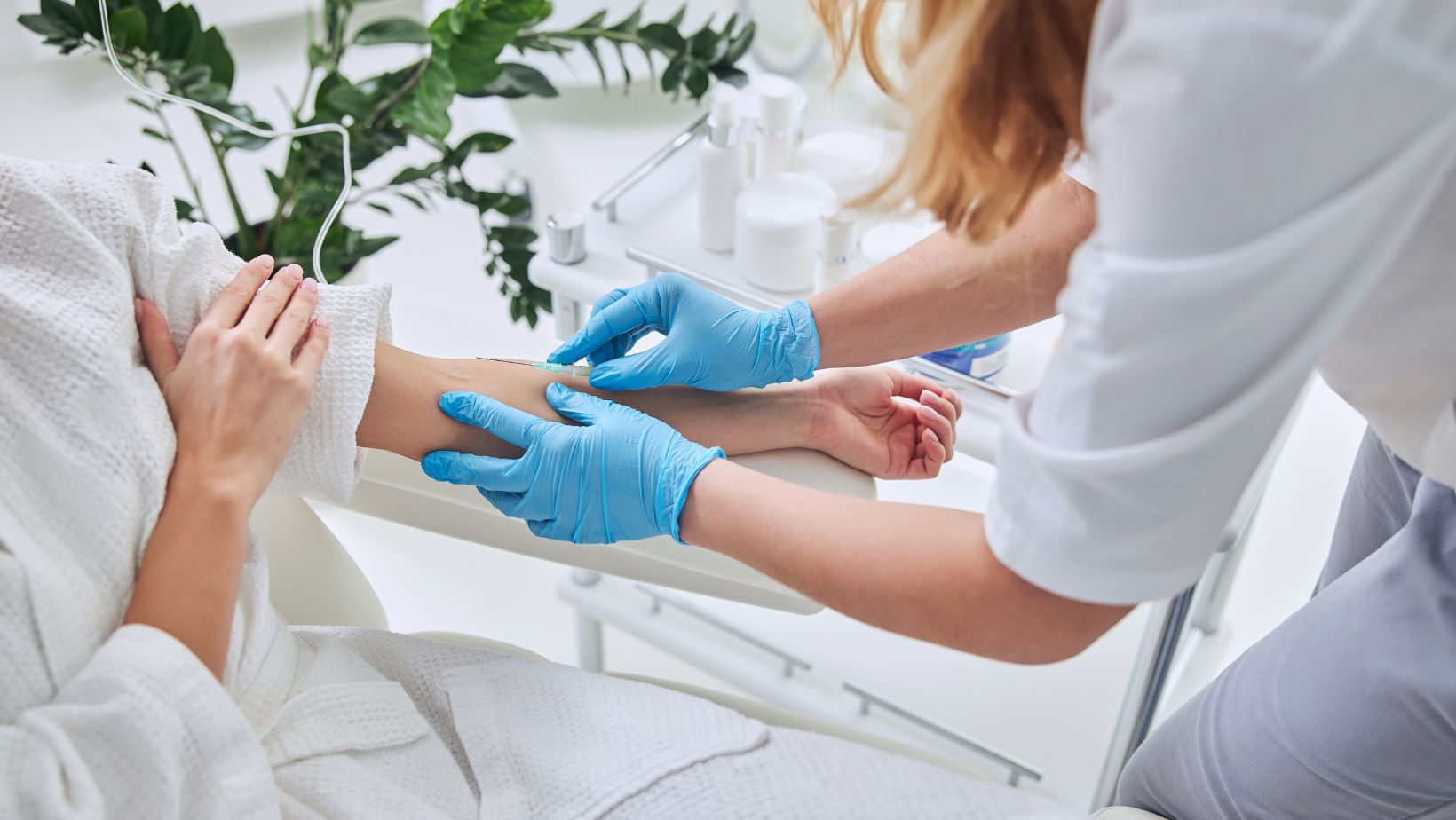
And here the severity depends on the type of medicine, the amount leaked, and how long it stays in the tissue. Chemical burns from IV infiltration can destroy cells and cause long-lasting tissue injury if not treated quickly.
Common Causes of IV Infiltration
There are some common causes that patients need to be aware of so they can take the necessary actions or get proper medical help.
Improper needle insertion or catheter placement: If the needle or catheter is not placed correctly, fluid can leak into nearby tissue.
Poor site monitoring and high infusion rates: Not checking the IV site regularly or using fast fluid flow can cause infiltration in some patients.
Patient movement and fragile veins: The movement can dislodge the IV, and weak veins are more likely to be damaged or leak and cause this.
What to Do If IV Infiltration Is Suspected
In case of suspected IV infiltration, stop the IV infusion immediately and notify a medical professional. Remove the IV catheter carefully to prevent further damage. Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain if advised. Seek medical evaluation to assess the extent of tissue damage. Treatment may involve wound care, pain management, and, in severe cases, surgery or reconstructive procedures.
If the injury is serious, consider reaching out to professional injury attorneys who can help protect your rights and provide legal support, because early action is important to prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
Conclusion
- IV infiltration can be very harmful if not treated quickly.
- It can cause pain, swelling, and damage to tissues.
- Some cases might need surgery or take a long time to heal.
- Checking the IV site regularly can help find problems early.
- Patients and caregivers should be aware of the signs and act quickly.
- If an injury happens, getting proper medical care is important to minimize damage.
- In serious cases, getting help from injury lawyers may be necessary to protect rights and get compensation.